WHAT IS MYOPIA?
Nearsightedness can be defined as having trouble seeing far away. Due to an increase in near-work demands and a decrease in time outdoors, myopia is on the rise. “Myopia Management” is the term used to describe specific treatments used to help slow the progression of near-sightedness in children by approximately 50% with few risks. Millions of children could benefit from slowing the progression of myopia due to the medical burden associated with higher risk of developing sight-threatening complications such as glaucoma, cataract, retinal degeneration, and retinal detachment. The four primary categories of myopia control treatments include the use of atropine eye drops, multifocal contact lenses, multifocal eyeglasses and orthokeratology.
Myopia In Children
The number of children that are becoming myopic (nearsighted) has been growing rapidly over the last 25 years and is expected to impair fully 50% of the world’s population by the year 2050. This rapid increase is due in part to children spending more time studying, reading and using the computer rather than playing outdoors. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) now views progressive myopia as an epidemic.
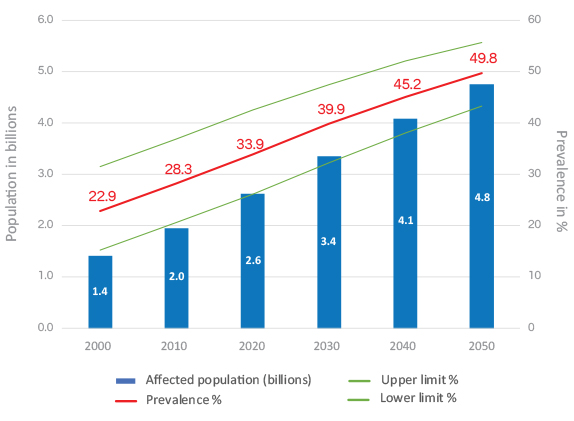
Almost 5 billion myopes by 2050
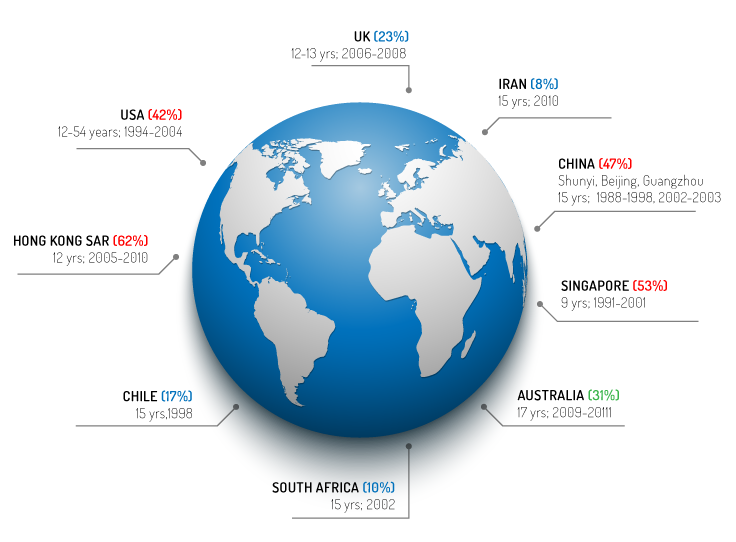
Recent research in Canada has shown that 6% of children between the ages of 6-8 and 28.9% of children between the ages of 11-13 were suffering from Myopia. Previously, myopia was very rare in children below the age of 11. Changes in lifestyle and kids spending more hours using smartphones and tablets have caused an increase in myopia prevalence. For one additional hour spent outdoors each week, the odds of being myopic were lowered by 14.3%.
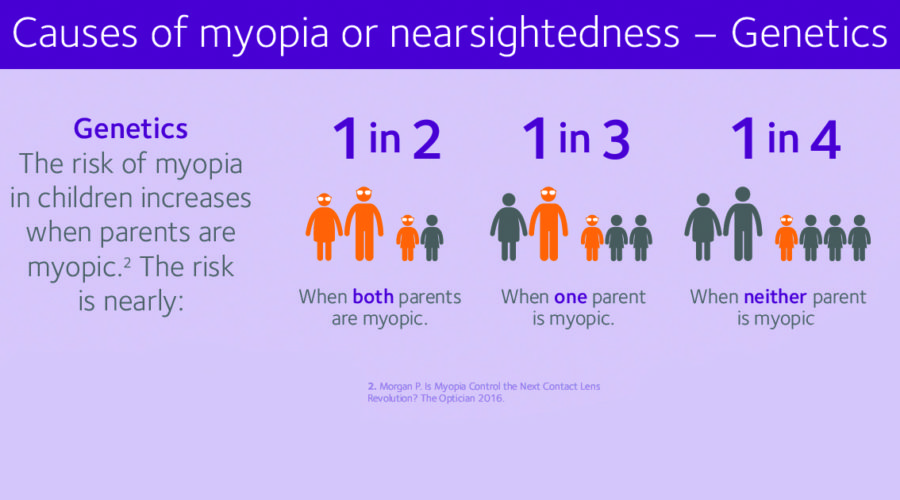
WHAT CAUSES MYOPIA
SIGNS OF MYOPIA
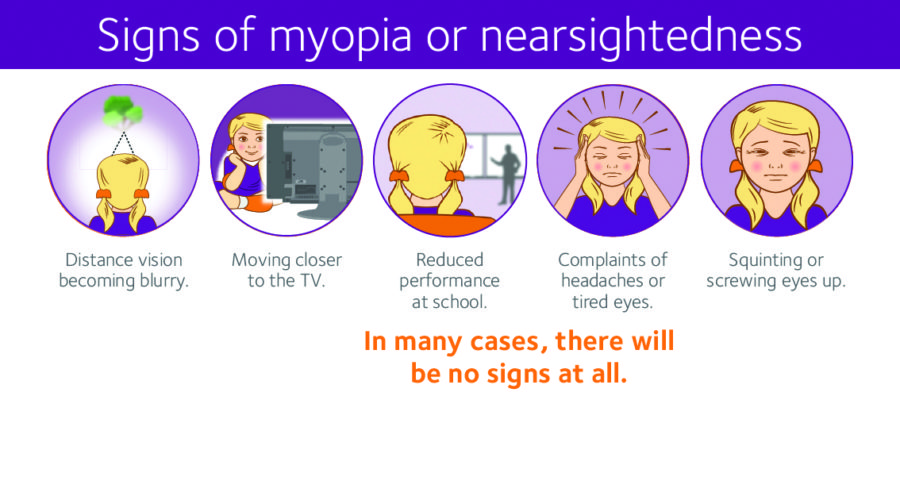
HOW CAN MYOPIA AFFECT MY CHILD?
Myopia Management Techniques
Until recently, the only treatment for paediatric myopia was glasses, with frequent prescription updates as vision gets worse.
Today, new innovative techniques for treatment include soft contact lenses, orthokeratology and using atropine drops. All these techniques, help by slowing down the axial elongation of a myopic eyeball.
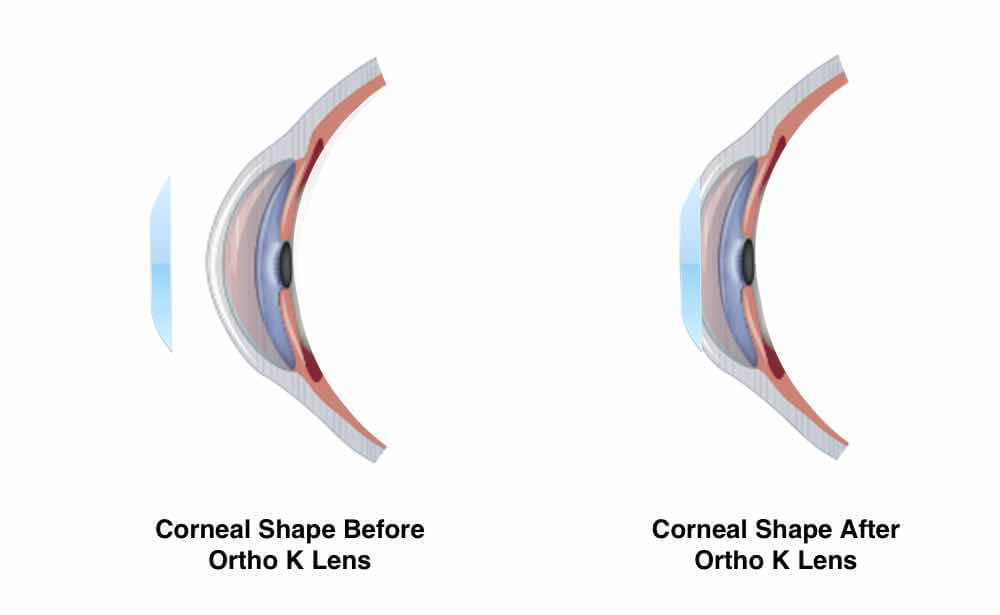
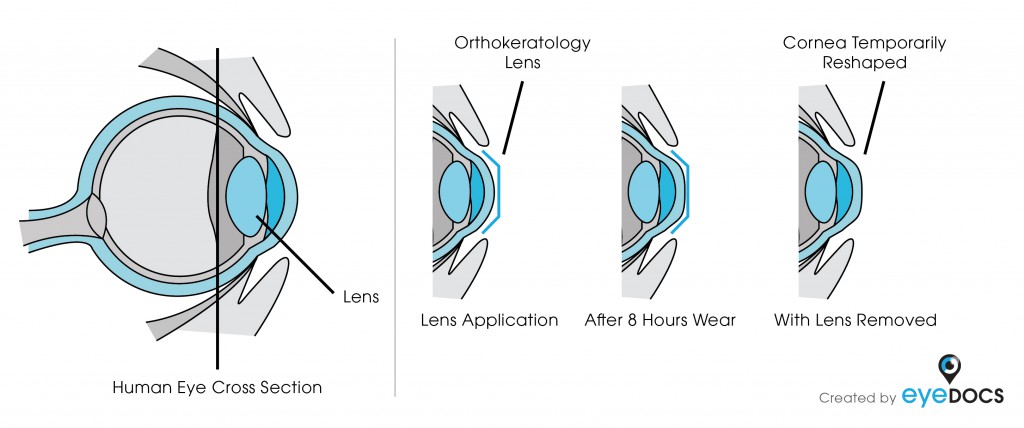
Orthokeratology
Orthokeratology is an innovative non-surgical procedure that eliminates the need for daytime contact lenses or glasses. It improves vision by gently reshaping your eye while you sleep using specially designed therapeutic contact lenses. You just put the specially fitted lenses in at bedtime, and when you awake, you will have clear, sharp, natural vision for your waking hours. This safe and effective treatment can correct near-sightedness (including high prescriptions).
Atropine Drops
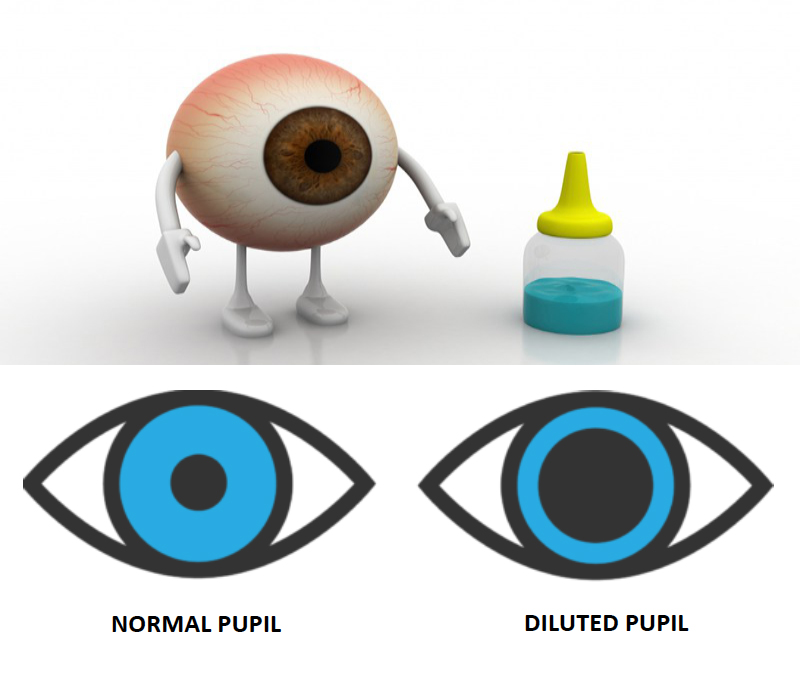
A promising treatment for childhood near-sightedness (myopia) is welcome news at a time when more and more kids are being diagnosed with the condition. Studies show that a low-dose of atropine, typically given as eye drops at bedtime, can significantly slow the progression of myopia in children, preventing severe near-sightedness.
Childhood myopia is usually diagnosed when kids are around 5 to 7 years old. Often, vision gets worse during the eye’s rapid growing years and levels off until the late stages of adolescence.
Myopia is a condition that isn’t reversible and will only get worse in the time since everything in the world has moved towards digital devices. However, these new innovative treatment options will help the child’s near-sightedness from progressing as opposed to those kids who haven’t received treatment.


